
Trillium develops software solutions for scientific purposes. Some of our programs are available for free download.
For inquiries regarding custom software development, please use the contact form
VeRIf: Verification of Reference Intervals
Topic: Verification and assessment of reference limits from routine laboratory results using the indirect methods reflimR and refineR as well as the machine learning package mclust.
Input: Numerical laboratory values
Output: Verified or estimated reference limits, respectively, with graphical output and status indicators
R Basics: First Steps
Georg Hoffmann
2022-07-04
Contents
- Background and installation
- Computing in the R console
- Generating and processing data
- Creating and formatting graphics
The software tool R has been available under a General Public License since 1995. With the establishment of the worldwide server network Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN) in 1998 and the non-profit R Foundation in 2002, the rapid success of this software and programming language began, particularly in the fields of statistics, bioinformatics, and data science. Today, R consistently ranks among the twenty most widely used programming languages in the world.
Simple Methods for Verifying Reference Intervals
Georg Hoffmann (1), Frank Klawonn (2)
2022-06-15
- Trillium GmbH Med. Fachverlag, Grafrath
- Helmholtzzentrum für Infektionsforschung (HZI), Braunschweig
Background and Objectives
According to national and international regulations, medical laboratories are required to verify all reference intervals (RI) that they have adopted from product inserts or other external sources (Sack U & Özçürümez M 2019, Hoffmann 2020) + Link. By definition, RIs are the central 95% of laboratory values measured in healthy reference individuals. However, guideline-compliant identification and recruitment of such individuals is often impractical in daily practice due to time and cost constraints.
Therefore, indirect methods are predominantly used today, which make it possible to identify “presumably non-pathological” values from routine data and to estimate their reference limits using mathematical parameters. This is organizationally much simpler than the direct methods, but requires additional statistical effort, which is often associated with long computation times and high requirements regarding case numbers.
This article deals with the pure verification of whether predefined reference limits fit the local conditions with regard to analytics and post-analytics or not. For this purpose, no such extensive effort should be made as for the de novo determination of reference intervals. Here, we present simple graphical procedures that make it possible, with low mathematical effort and moderate case numbers, to check which reference intervals can be accepted in the laboratory information system and which require correction.
Statistics
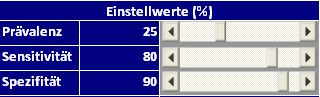
Four-field-table/Bayes´theorem
Topic: Evaluation of diagnostic tests
Input: Prevalence, sensitivity, specificity
Output: Predictive values (nPV, pPV)
Special features: Excel worksheet with sliders for adjusting the input values
RefLim: Excel program for calculating reference intervals
RefLim
Topic: Estimation and verification of reference intervals
Input: Laboratory values in Excel and text formats (.xls, .xlsx, .csv, .txt)
Output: Commented reference intervals
Requirements: MS Excel on Windows (not macOS, Linux, etc.)*
Special features: Evaluation of routine laboratory data with up to 20% pathological values possible.
*The xlsm file contains macros that must be enabled at startup. You may receive a firewall warning, which you must accept in order to download the program.


